Today we are going to learn about one of the primary pillar of OOPS i.e Inheritance.
So let's start with the overview.
Overview: - Inheritance is one of the four primary characteristics (or pillars) of object-oriented programming. Inheritance provide the capabilities to add new feature in a class by using existing class.
Inheritance allow us to create new classes that can be reuse, extend, and modify the behavior that is already defined in other classes.
A class whose members are inherited is called the base class/parent class/super class, and the class that is inherits those members base class is called the derived class/child class/sub class.
For Example: - Animal is a base class and Dog, Cow etc. are the child or derived classes.
Advantage: -
- Provides code reusability.
- Reduces source code size and improves code readability.
- Code is easy to manage and divided into parent and child classes.
- Supports code extensibility by overriding the base class functionality within child classes.
- In Inheritance base class and child classes are tightly coupled. Hence If you change the code of parent class, it will get affects to the all the child classes.
- In class hierarchy many data members remain unused and the memory allocated to them is not utilized. Hence affect performance of your program if you have not implemented inheritance correctly.
//Base Class
public class Employee
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Email { get; set; }
public DateTime DateofBirth { get; set; }
}
//Child Class1
public class PermanetEmployee : Employee
{
public double SalaryPerDays { get; set; }
public int WorkingDays { get; set; }
public double getPermanetEmployeeSalary()
{
return SalaryPerDays * WorkingDays;
}
}
//Child Class2
public class ContactEmployee : Employee
{
public double SalaryPerHours { get; set; }
public int WorkingHours { get; set; }
public double getContactEmployeeSalary()
{
return SalaryPerHours * WorkingHours;
}
}
public static class Test
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
PermanetEmployee permanetEmployee = new PermanetEmployee();
//reusable code
permanetEmployee.ID = 1;
permanetEmployee.Name = "Tom";
permanetEmployee.Email = "tom@test.com";
permanetEmployee.DateofBirth = DateTime.Now;
//new code for Permanet Employee
permanetEmployee.SalaryPerDays = 1400;
permanetEmployee.WorkingDays = 28;
var PermanetEmployeeSalary = permanetEmployee.getPermanetEmployeeSalary();
Console.WriteLine("PermanetEmployee Salary:{0}", PermanetEmployeeSalary);
ContactEmployee contactEmployee = new ContactEmployee();
//reusable code
contactEmployee.ID = 1;
contactEmployee.Name = "Tom";
contactEmployee.Email = "tom@test.com";
contactEmployee.DateofBirth = DateTime.Now;
//new code for contract Employee
contactEmployee.SalaryPerHours = 100;
contactEmployee.WorkingHours = 54;
var ContactEmployeeSalary = contactEmployee.getContactEmployeeSalary();
Console.WriteLine("ContactEmployee Salary:{0}", ContactEmployeeSalary);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
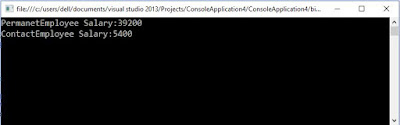
Output:PermanetEmployee Salary:39200
ContactEmployee Salary:5400
 |
| Salaries of each Employee type |
- Single inheritance
- Multi-level inheritance
- Hierarchical inheritance
- Hybrid inheritance
Virtual Keyword
It used to allow a method can be overridden by child classes.
example:
public virtual int myValue()
{
//To DO
}
Override Keyword
It used to override the parent class method when method declared under abstract class method or marked as virtual in normal parent class. It is also known as Method overriding.
example:
public override int myValue()
{
//To DO
}
Base Keyword
It used to calls parent class method from child class for overriding functionality.
example:
public void int myValue()
{
base.NewValue();
}
New Keyword
Used to hide the base class member when a method name and signature is same in parent as well child class. It is also known as Method hiding.
example:
public new int myValue()
{
//To DO
}
Basic and Important Rules of Inheritance
public class OverridingDemo1
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Case:-1
ParentClass p1 = new ParentClass();
p1.ParentMethod(); //valid
p1.ChildMethod(); //invalid: because by base class object we can not call child class member.
//Case:-2:by child class object we can called parent class member and parent class member
ChildClass c1 = new ChildClass();
c1.ParentMethod(); //valid
c1.ChildMethod(); //valid.
//Case:-3:
ParentClass pc = new ChildClass(); //parent class variable can hold the reference of child class
pc.ParentMethod(); //valid
pc.ChildMethod(); //invalid: because by parent class object we can not call child class member.
//Case:-4:
ChildClass cp = new ParentClass(); //child class variable can hold the reference of parent class
}
}
public class ParentClass
{
public void ParentMethod()
{
Console.WriteLine("ParentClass with ParentMethod() is called");
}
}
public class ChildClass : ParentClass
{
public void ChildMethod()
{
Console.WriteLine("ChildClass with ChildMethod() is called");
}
}
Summary:So, Guys that's all about Inheritance in C#. In our next post we will be learning Polymorphism and its types.
I Hope in this post I have covered all the points about Inheritance which will be helpful to you.
Please share this post with your friends and colleagues.
For any queries please post a comment below.
Happy Coding 😉


0 comments:
Post a Comment
If you like this website, please share with your friends on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn.