In this article, I am going to discuss the Entity Framework Context Class with an example. Please read our previous article where we discussed the Architecture of Entity Framework in Detail. At the end of this article, you will understand what exactly the Context Class is and when and how to use this Context Class in Entity Framework with an example.
What is Context Class in Entity Framework?
The Entity Framework enables us to query, insert, update, and delete data using Common Language Runtime (CLR) objects which are also known as entities. The Entity Framework maps the entities and relationships that are defined in our model to a database.
The primary class that is responsible for interacting with data as objects is System.Data.Entity.DbContext. The context class in Entity Framework is a class that derives from DBContext in EF 6 and EF Core both. It is an important class in Entity Framework, which represents a session with the underlying database.
We are going to work with the same example that we created in our Introduction to Entity Framework article. In that console application, we retrieve the data from a SQL Server database using Entity Framework.
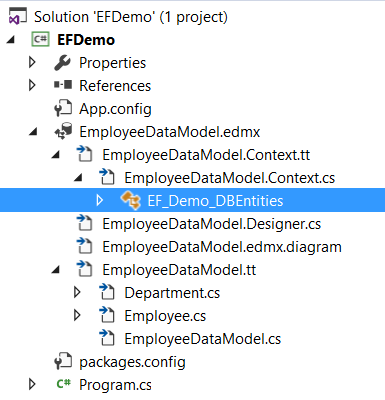
First, let’s have a look at the solution. Please double click on the EF_Demo_DBEntities which is inside the EmployeeDataModel.Context.cs which is inside EmployeeDataModel.Context.tt file as shown below.
The following EF_Demo_DBEntities class is an example of a context class which is created by Entity Framework.
The context class is used to query or save data to the database. It is also used to configure domain classes, database-related mappings, change tracking settings, caching, transaction, etc. which we will discuss in detail in our upcoming articles.
How to query using Context Class?
Modify the Program class as shown below.
In the next article, I am going to discuss the Entities in Entity Framework. Here, in this article, I try to explain the Context class in Entity Framework with one example. I hope this article will help you with your need. I would like to have your feedback. Please post your feedback, question, or comments about this article
Summary:
I hope this post will be helpful to understand the Entity Framework Context Class
Please share this post with your friends and colleagues.
For any queries please post a comment below.
Happy Coding 😉
What is Context Class in Entity Framework?
The Entity Framework enables us to query, insert, update, and delete data using Common Language Runtime (CLR) objects which are also known as entities. The Entity Framework maps the entities and relationships that are defined in our model to a database.
The primary class that is responsible for interacting with data as objects is System.Data.Entity.DbContext. The context class in Entity Framework is a class that derives from DBContext in EF 6 and EF Core both. It is an important class in Entity Framework, which represents a session with the underlying database.
We are going to work with the same example that we created in our Introduction to Entity Framework article. In that console application, we retrieve the data from a SQL Server database using Entity Framework.
First, let’s have a look at the solution. Please double click on the EF_Demo_DBEntities which is inside the EmployeeDataModel.Context.cs which is inside EmployeeDataModel.Context.tt file as shown below.
The following EF_Demo_DBEntities class is an example of a context class which is created by Entity Framework.
namespace EFDemo
{
using System;
using System.Data.Entity;
using System.Data.Entity.Infrastructure;
public partial class EF_Demo_DBEntities : DbContext
{
public EF_Demo_DBEntities()
: base("name=EF_Demo_DBEntities")
{
}
protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
throw new UnintentionalCodeFirstException();
}
public virtual DbSet<Department> Departments { get; set; }
public virtual DbSet<Employee> Employees { get; set; }
}
}
In the above example, the EF_Demo_DBEntities class is derived from the DbContext class which makes it a context class. It also includes an entity set for Departments and Employees entities.
The context class is used to query or save data to the database. It is also used to configure domain classes, database-related mappings, change tracking settings, caching, transaction, etc. which we will discuss in detail in our upcoming articles.
How to query using Context Class?
Modify the Program class as shown below.
namespace EFDemo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
using (EF_Demo_DBEntities DBEntities = new EF_Demo_DBEntities())
{
List<Department> listDepartments = DBEntities.Departments.ToList();
Console.WriteLine();
foreach(Department dept in listDepartments)
{
Console.WriteLine(" Department = {0}, Location = {1}", dept.Name, dept.Location);
foreach(Employee emp in dept.Employees)
{
Console.WriteLine("\t Name = {0}, Email = {1}, Gender = {2}, salary = {3}",
emp.Name, emp.Email, emp.Gender, emp.Salary);
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
}
Run the application and see the results. We will discuss more the Context class in a later article.
In the next article, I am going to discuss the Entities in Entity Framework. Here, in this article, I try to explain the Context class in Entity Framework with one example. I hope this article will help you with your need. I would like to have your feedback. Please post your feedback, question, or comments about this article
Summary:
I hope this post will be helpful to understand the Entity Framework Context Class
Please share this post with your friends and colleagues.
For any queries please post a comment below.
Happy Coding 😉


0 comments:
Post a Comment
If you like this website, please share with your friends on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn.