In this article, I am going to discuss Blazor Project Structure in detail. Please read our previous article, where we discussed the Blazor Hosting Models. At the end of this article, you will understand the need and use of different files and folders of the Blazor application.
ASP.NET Core Blazor Project Structure:
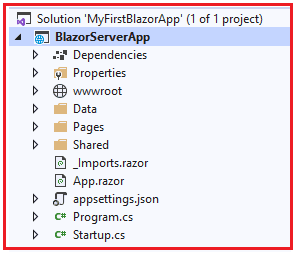
In part 3 of this article series, we created one solution with two projects. The following is the structure.
Now, let us discuss the files and folders one by one.
Program.cs
This file contains the Main() method which is the entry point for both the project types (i.e Blazor WebAssembly and Blazor Server).
In a Blazor server project, the Main() method calls CreateHostBuilder() method which sets up the ASP.NET Core host.
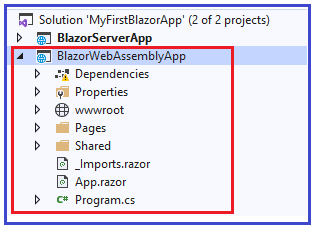
In a Blazor WebAssembly project, the App component, which is the root component of the application, is specified in the Main method. This root component is present in the root project folder in the App.razor file.
Components are the building blocks of a Blazor application. We will discuss everything you need to know to build effective and reusable blazor components in our upcoming videos. For now, just understand the App component is the root component of the application.
wwwroot
For both the project types, this folder contains static files like images, stylesheets, etc.
App.razor
This is the root component of the application. It uses the built-in Router component and sets up client-side routing. It is this Router component that intercepts browser navigation and renders the page that matches the requested address. The Router uses the Found property to display the content when a match is found. If a match is not found, the NotFound property is used to display the message – Sorry, there’s nothing at this address.
Pages folder
This folder contains the _Host razor page and the routable components that make up the Blazor app. The components have the .razor extension.
As the name implies, contains the shared components
MainLayout component (MainLayout.razor)
The application’s main layout component
NavMenu component (NavMenu.razor)
Implements the navigation menu on the sidebar. NavLink component renders navigation links to other Razor components like the index, counter, and fetchdata components. This NavLink component is intelligent enough to highlight the navigation menu item if it’s component is currently displayed.
_Imports.razor
This is like _ViewImports.cshtml file in an asp.net core MVC project. This file contains the common namespaces so we do not have to include them in every razor component.
wwwroot/index.html
This is the root page in a Blazor WebAssembly project and is implemented as an HTML page. When a first request hits the application, it is this page, that is initially served. It has the standard HTML, HEAD, and BODY tags. It specifies where the root application component App.razor should be rendered. You can find this App.razor root component in the root project folder. It is included on the page as an HTML element.
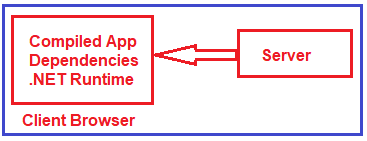
This index.html page also loads the blazor WebAssembly JavaScript file (_framework/blazor.webassembly.js). It is this file that is responsible for downloading
The compiled blazor application, it’s dependencies, and the .NET runtime. It also initializes the runtime to run the blazor app in the browser
Startup.cs
This file is present only in the Blazor Server project. As the name implies it contains the applications’ startup logic. The Startup class contains the following two methods.
ConfigureServices – Configures the applications DI i.e dependency injection services. For example, AddServerSideBlazor() method adds Blazor server-side services. On the IServiceCollection interface, there are several methods that start with the word Add. These methods add different services for the Blazor application. We can even add our own services to the DI container. We will see this in action in our upcoming videos.
Configure – Configures the app’s request processing pipeline. Depending on what we want the Blazor application to be capable of doing we add or remove the respective middleware components from the request processing pipeline. For example, UseStaticFiles() method adds the middleware component that can serve static files like images, CSS, etc.
MapBlazorHub sets up the endpoint for the SignalR connection with the client browser.
Pages/_Host.cshtml
This is the root page of the application and is specified by calling MapFallbackToPage(“/_Host”) method. It is implemented as a razor page.
It is this page, that is initially served when a first request hits the application. It has the standard HTML, HEAD, and BODY tags. It also specifies where the root application component, App component (App.razor) must be rendered. Finally, it also loads the blazor.server.js JavaScript file, which sets up the real-time SignalR connection between the server and the client browser. This connection is used to exchange information between the client and the server. SignalR is a great framework for adding real-time web functionality to apps.
The data folder (Blazor Server)
Contains code files related to the sample WeatherForecast service
appsettings.json (Blazor Server)
Just like an asp.net core MVC project, a blazor project also uses this file to store the configuration settings.
Here, in this article, I try to explain the Blazor Project Structure in Detail. I hope now you got some idea regarding the files and folders of the ASP.NET Core Blazor App.
Summary:
I hope this post will be helpful to understand the Blazor Project Structure
Please share this post with your friends and colleagues.
For any queries please post a comment below.
Happy Coding 😉
ASP.NET Core Blazor Project Structure:
In part 3 of this article series, we created one solution with two projects. The following is the structure.
Now, let us discuss the files and folders one by one.
Program.cs
This file contains the Main() method which is the entry point for both the project types (i.e Blazor WebAssembly and Blazor Server).
In a Blazor server project, the Main() method calls CreateHostBuilder() method which sets up the ASP.NET Core host.
In a Blazor WebAssembly project, the App component, which is the root component of the application, is specified in the Main method. This root component is present in the root project folder in the App.razor file.
Components are the building blocks of a Blazor application. We will discuss everything you need to know to build effective and reusable blazor components in our upcoming videos. For now, just understand the App component is the root component of the application.
wwwroot
For both the project types, this folder contains static files like images, stylesheets, etc.
App.razor
This is the root component of the application. It uses the built-in Router component and sets up client-side routing. It is this Router component that intercepts browser navigation and renders the page that matches the requested address. The Router uses the Found property to display the content when a match is found. If a match is not found, the NotFound property is used to display the message – Sorry, there’s nothing at this address.
Pages folder
This folder contains the _Host razor page and the routable components that make up the Blazor app. The components have the .razor extension.
-
Index component (Index.razor) – Rendered when we navigate to the root application URL.
Counter component (Counter.razor) – Rendered when we navigate to the path /counter.
FetchData component (FetchData.razor) – Rendered when we navigate to the path /fetchdata.
Error component (Error.razor) – Rendered when an unhandled exception occurs in the blazor app.
As the name implies, contains the shared components
MainLayout component (MainLayout.razor)
The application’s main layout component
NavMenu component (NavMenu.razor)
Implements the navigation menu on the sidebar. NavLink component renders navigation links to other Razor components like the index, counter, and fetchdata components. This NavLink component is intelligent enough to highlight the navigation menu item if it’s component is currently displayed.
_Imports.razor
This is like _ViewImports.cshtml file in an asp.net core MVC project. This file contains the common namespaces so we do not have to include them in every razor component.
wwwroot/index.html
This is the root page in a Blazor WebAssembly project and is implemented as an HTML page. When a first request hits the application, it is this page, that is initially served. It has the standard HTML, HEAD, and BODY tags. It specifies where the root application component App.razor should be rendered. You can find this App.razor root component in the root project folder. It is included on the page as an HTML element
This index.html page also loads the blazor WebAssembly JavaScript file (_framework/blazor.webassembly.js). It is this file that is responsible for downloading
The compiled blazor application, it’s dependencies, and the .NET runtime. It also initializes the runtime to run the blazor app in the browser
Startup.cs
This file is present only in the Blazor Server project. As the name implies it contains the applications’ startup logic. The Startup class contains the following two methods.
ConfigureServices – Configures the applications DI i.e dependency injection services. For example, AddServerSideBlazor() method adds Blazor server-side services. On the IServiceCollection interface, there are several methods that start with the word Add. These methods add different services for the Blazor application. We can even add our own services to the DI container. We will see this in action in our upcoming videos.
Configure – Configures the app’s request processing pipeline. Depending on what we want the Blazor application to be capable of doing we add or remove the respective middleware components from the request processing pipeline. For example, UseStaticFiles() method adds the middleware component that can serve static files like images, CSS, etc.
MapBlazorHub sets up the endpoint for the SignalR connection with the client browser.
Pages/_Host.cshtml
This is the root page of the application and is specified by calling MapFallbackToPage(“/_Host”) method. It is implemented as a razor page.
It is this page, that is initially served when a first request hits the application. It has the standard HTML, HEAD, and BODY tags. It also specifies where the root application component, App component (App.razor) must be rendered. Finally, it also loads the blazor.server.js JavaScript file, which sets up the real-time SignalR connection between the server and the client browser. This connection is used to exchange information between the client and the server. SignalR is a great framework for adding real-time web functionality to apps.
The data folder (Blazor Server)
Contains code files related to the sample WeatherForecast service
appsettings.json (Blazor Server)
Just like an asp.net core MVC project, a blazor project also uses this file to store the configuration settings.
Here, in this article, I try to explain the Blazor Project Structure in Detail. I hope now you got some idea regarding the files and folders of the ASP.NET Core Blazor App.
Summary:
I hope this post will be helpful to understand the Blazor Project Structure
Please share this post with your friends and colleagues.
For any queries please post a comment below.
Happy Coding 😉