In this article, I am going to discuss the step by step procedure for Creating Web API Application. Please read my previous article What is Web API before proceeding to this article where we have gone through the ASP.NET Web API framework.
Creating Web API Application using Visual Studio:
First, open the Visual Studio and then select File -> New Project as shown in the below image.
In the “New Project” window Select “Visual C#” under the “Installed – Templates” and From the middle pane select the ASP.NET Web Application and name the project as “FirstWebAPIDemo” and then click on the “OK” button as shown in the below image.
Once you click on the OK button, then a new window will open with Name New ASP.NET Project for selecting project Templates and from that window select the Web API project template and click on the OK button as shown in the below image.
Once you click on the OK button, It will take some time to create the project for us.
Understanding the Folder Structure of Web API Application:
If you have worked with ASP.NET MVC Framework, then the project folder structure should be familiar to you as shown below.
Here, we have separate folders for Models, Views, and Controllers and moreover, within the Controllers folder, we have both MVC as well as Web API Controller as shown in the below image.
The important thing to keep in mind is that the Web API Controllers are different from MVC Controllers. In our example, the ValuesController is WebAPI Controller.
If you observe the above ValuesController Class, then you will see that it inherits from the ApiController class which is present in sytem.web.http namespace.
Further, if you notice that the HomeController class is an MVC Controller, which is inherited from the Controller class that is present in System.Web.Mvc namespace as shown in the below image.
Here we are going to focus on the Web API controller (i.e. Values Controller).
Notice that in the ValuesController we have methods such as Get, Put, Post and Delete that map to the HTTP verbs GET, PUT, POST and DELETE respectively as shown in below image.
We have 2 overloaded versions of the Get() method – One method without any parameters and the other one with the id parameter. Both of these methods respond to the GET HTTP verb depending on whether the id parameter is passed or not in the URL.
Now let’s look at the default route for our Web API project. We have the Application_Start() method within the Global.asax file. This method is executed when the application starts for the first time. In the Application_Start() method we have the configuration for Filters, Bundles, etc. as shown below.
The one that we are interested in here is the configuration for our Web API project, which is in WebApiConfig.Register() method. So right-click on the WebApiConfig.Register method and then select the “Go To Definition” from the context menu which will take you to the Register() method of the WebApiConfig class as shown below.
This class is in the App_Start folder.
You can see a default route is configured within the Register() method for our Web API project. The Web API routes are different from the MVC routes. You can find the MVC routes in RouteConfig.cs file which is present in the App_Start folder.
The default route in Web API starts with the word API followed by a / and then the name of the controller and then another / and an optional id parameter as shown below.
“api/{controller}/{id}”
At this point, if you use the following URI in the browser, you will get an error stating – Authorization has been denied for this request.
http://localhost:xxxxx/api/values
To get rid of this error, comment Authorize attribute on the ValuesController class. This is related to security which we will discuss in a later article.
Now if you issue the URI http://localhost:xxxxx/api/values in the browser, then you should see the following XML as the result
Let us understand what is going on here.
The name of the controller is “values“. So if you issue a URI http://localhost:portnumber/api/values, then the Web API Framework is going to look for a controller with name Values + the word controller i.e. ValuesController in your application.
So if you have specified values in the URI it is going to look for ValuesController, if you specify Products, then it is going to look for ProductsController.
In a real-world application, this might be the domain name, for example, https://csharptechtics.blogspot.com/api/values The browser is issuing a GET request which maps to the Get() method in the ValuesController class. The GET() in the values controller is returning value1 and value2 which is what we see in the browser.
We have another overload of GET() method within the Values Controller which takes the Id parameter. If you remember with the default route within the WebApiConfig file, we specified the id parameter is optional. This is the reason why we are able to call the GET method with or without the Id parameter. So, if you specified the id parameter in the URI, then, the Get() method with the id parameter in values controller is going to be called
If a controller with the specified name is not found by the Web API Framework, then the Framework will an error. For example, in our application, if we comment “ValuesController” class in our project and then use the URI /api/values then you will get the following error
No HTTP resource was found that matches the request URI ‘http://localhost:15648/api/values’. No type was found that matches the controller named ‘values’.
Let’s discuss about POST, PUT and DELETE.
In a database table row, we can perform the following 4 actions
From the ASP.NET Web API point of view, these 4 actions correspond to GET, POST, PUT and DELETE verb as shown below
Let us discuss some terms and concepts which are related to HTTP request and response.
Request Verbs:
The HTTP verbs such as GET, POST, PUT and DELETE describe what should be done with the Web API resource. For example, do you need to read, create, update or delete an entity? The HTTP Verbs GET, PUT, POST and DELETE are the most commonly used verbs in real-time applications. For the list of the complete HTTP verbs, please check the following URL
http://www.w3.org/Protocols/rfc2616/rfc2616-sec9.html
Request Header:
When a client sends the request to the server, the request contains a header and a body. The header of the request contains some additional information such as what type of response the client required. For example, the client wants the response to be in XML or JSON format.
Request Body:
The Request Body contains the data that you want to send to the server. For example, a POST request contains the data in the Request Body for the new item that you want to create. The data may be in the form XML or JSON.
Response Body:
The Response Body contains the data that is sent as a response from the server. For example, if you request a specific employee, then the response body includes the employee details either in the form of XML or JSON.
Response Status codes:
The Response Status Codes are the HTTP status codes that will specify the status of the request. The most common status codes are 200/OK, 204/No Content, 500/Internal Server Error, 404/Not Found. If you want to see the complete list of HTTP status codes then please follow the below
http://www.w3.org/Protocols/rfc2616/rfc2616-sec9.html
To perform the GET, POST, PUT & DELETE actions, we will use a tool called Fiddler. You can download fiddler from the following link
https://www.telerik.com/download/fiddler
Modify the ValuesController as shown below, so that it can support POST, PUT and DELETE actions.
Summary:
I Hope this post will be helpful to understand How to create a Web API application.
Please share this post with your friends and colleagues.
For any queries please post a comment below.
Happy Coding 😉
Creating Web API Application using Visual Studio:
First, open the Visual Studio and then select File -> New Project as shown in the below image.
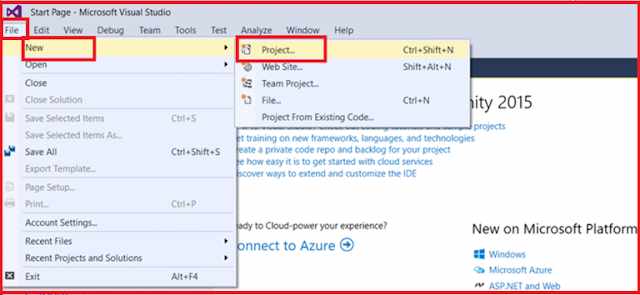 |
| Creating new Web API Application |
In the “New Project” window Select “Visual C#” under the “Installed – Templates” and From the middle pane select the ASP.NET Web Application and name the project as “FirstWebAPIDemo” and then click on the “OK” button as shown in the below image.
 |
| Selecting Project Template |
Once you click on the OK button, then a new window will open with Name New ASP.NET Project for selecting project Templates and from that window select the Web API project template and click on the OK button as shown in the below image.
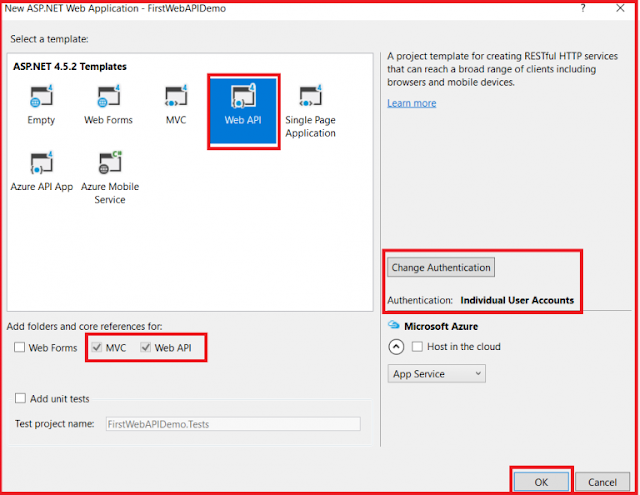 |
| Selecting Web API Template |
Once you click on the OK button, It will take some time to create the project for us.
Understanding the Folder Structure of Web API Application:
If you have worked with ASP.NET MVC Framework, then the project folder structure should be familiar to you as shown below.
 |
| Web API Project Structure |
Here, we have separate folders for Models, Views, and Controllers and moreover, within the Controllers folder, we have both MVC as well as Web API Controller as shown in the below image.
 |
| Controllers |
The important thing to keep in mind is that the Web API Controllers are different from MVC Controllers. In our example, the ValuesController is WebAPI Controller.
 |
| Web API Controller |
If you observe the above ValuesController Class, then you will see that it inherits from the ApiController class which is present in sytem.web.http namespace.
Further, if you notice that the HomeController class is an MVC Controller, which is inherited from the Controller class that is present in System.Web.Mvc namespace as shown in the below image.
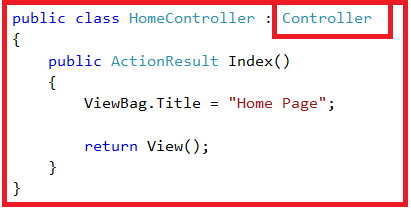 |
| MVC Controller |
Here we are going to focus on the Web API controller (i.e. Values Controller).
Notice that in the ValuesController we have methods such as Get, Put, Post and Delete that map to the HTTP verbs GET, PUT, POST and DELETE respectively as shown in below image.
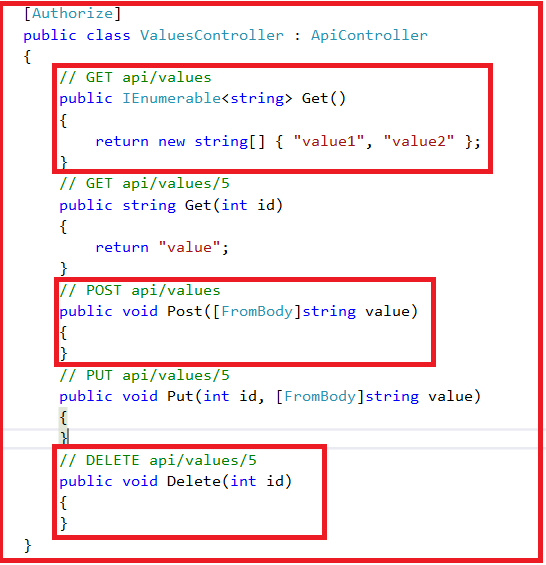 |
| Action Methods of values controller |
We have 2 overloaded versions of the Get() method – One method without any parameters and the other one with the id parameter. Both of these methods respond to the GET HTTP verb depending on whether the id parameter is passed or not in the URL.
Now let’s look at the default route for our Web API project. We have the Application_Start() method within the Global.asax file. This method is executed when the application starts for the first time. In the Application_Start() method we have the configuration for Filters, Bundles, etc. as shown below.
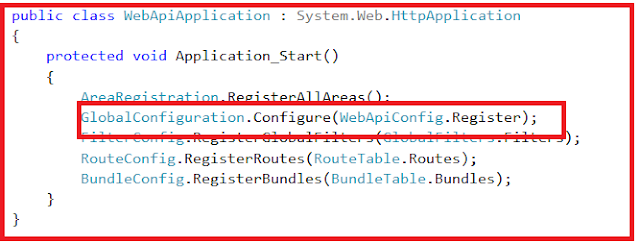 |
| Application Start Event |
The one that we are interested in here is the configuration for our Web API project, which is in WebApiConfig.Register() method. So right-click on the WebApiConfig.Register method and then select the “Go To Definition” from the context menu which will take you to the Register() method of the WebApiConfig class as shown below.
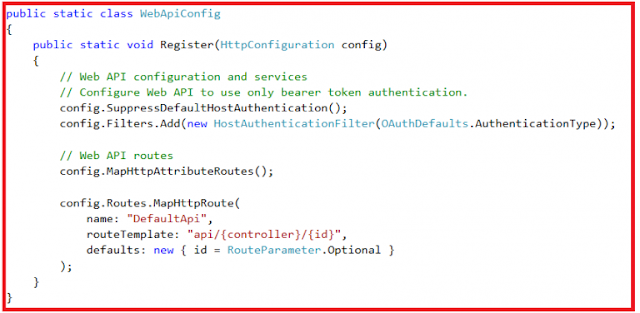 |
| Web API Config File |
This class is in the App_Start folder.
You can see a default route is configured within the Register() method for our Web API project. The Web API routes are different from the MVC routes. You can find the MVC routes in RouteConfig.cs file which is present in the App_Start folder.
The default route in Web API starts with the word API followed by a / and then the name of the controller and then another / and an optional id parameter as shown below.
“api/{controller}/{id}”
At this point, if you use the following URI in the browser, you will get an error stating – Authorization has been denied for this request.
http://localhost:xxxxx/api/values
To get rid of this error, comment Authorize attribute on the ValuesController class. This is related to security which we will discuss in a later article.
Now if you issue the URI http://localhost:xxxxx/api/values in the browser, then you should see the following XML as the result
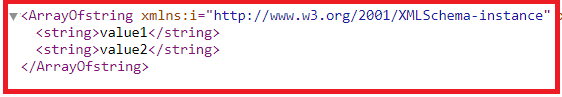 |
| Web API Response |
Let us understand what is going on here.
The name of the controller is “values“. So if you issue a URI http://localhost:portnumber/api/values, then the Web API Framework is going to look for a controller with name Values + the word controller i.e. ValuesController in your application.
So if you have specified values in the URI it is going to look for ValuesController, if you specify Products, then it is going to look for ProductsController.
In a real-world application, this might be the domain name, for example, https://csharptechtics.blogspot.com/api/values The browser is issuing a GET request which maps to the Get() method in the ValuesController class. The GET() in the values controller is returning value1 and value2 which is what we see in the browser.
We have another overload of GET() method within the Values Controller which takes the Id parameter. If you remember with the default route within the WebApiConfig file, we specified the id parameter is optional. This is the reason why we are able to call the GET method with or without the Id parameter. So, if you specified the id parameter in the URI, then, the Get() method with the id parameter in values controller is going to be called
If a controller with the specified name is not found by the Web API Framework, then the Framework will an error. For example, in our application, if we comment “ValuesController” class in our project and then use the URI /api/values then you will get the following error
No HTTP resource was found that matches the request URI ‘http://localhost:15648/api/values’. No type was found that matches the controller named ‘values’.
Let’s discuss about POST, PUT and DELETE.
In a database table row, we can perform the following 4 actions
 |
| CRUD Operations |
From the ASP.NET Web API point of view, these 4 actions correspond to GET, POST, PUT and DELETE verb as shown below
 |
| HTTP Verbs |
Let us discuss some terms and concepts which are related to HTTP request and response.
Request Verbs:
The HTTP verbs such as GET, POST, PUT and DELETE describe what should be done with the Web API resource. For example, do you need to read, create, update or delete an entity? The HTTP Verbs GET, PUT, POST and DELETE are the most commonly used verbs in real-time applications. For the list of the complete HTTP verbs, please check the following URL
http://www.w3.org/Protocols/rfc2616/rfc2616-sec9.html
Request Header:
When a client sends the request to the server, the request contains a header and a body. The header of the request contains some additional information such as what type of response the client required. For example, the client wants the response to be in XML or JSON format.
Request Body:
The Request Body contains the data that you want to send to the server. For example, a POST request contains the data in the Request Body for the new item that you want to create. The data may be in the form XML or JSON.
Response Body:
The Response Body contains the data that is sent as a response from the server. For example, if you request a specific employee, then the response body includes the employee details either in the form of XML or JSON.
Response Status codes:
The Response Status Codes are the HTTP status codes that will specify the status of the request. The most common status codes are 200/OK, 204/No Content, 500/Internal Server Error, 404/Not Found. If you want to see the complete list of HTTP status codes then please follow the below
http://www.w3.org/Protocols/rfc2616/rfc2616-sec9.html
To perform the GET, POST, PUT & DELETE actions, we will use a tool called Fiddler. You can download fiddler from the following link
https://www.telerik.com/download/fiddler
Modify the ValuesController as shown below, so that it can support POST, PUT and DELETE actions.
public class ValuesController : ApiController
{
static List<string> strings = new List<string>()
{
"value0", "value1", "value2"
};
// GET api/values
public IEnumerable<string> Get()
{
return strings;
}
// GET api/values/5
public string Get(int id)
{
return strings[id];
}
// POST api/values
public void Post([FromBody]string value)
{
strings.Add(value);
}
// PUT api/values/5
public void Put(int id, [FromBody]string value)
{
strings[id] = value;
}
// DELETE api/values/5
public void Delete(int id)
{
strings.RemoveAt(id);
}
}
At the moment the Post(), Put() and Delete() methods in the ValuesController are returning void. That is the reason why we are getting the status code 204 No Content. In ASP.NET Web API, an action method that returns void will send the status code 204 No Content by default, but we can control this behavior which we will discuss in a later article.
Summary:
I Hope this post will be helpful to understand How to create a Web API application.
Please share this post with your friends and colleagues.
For any queries please post a comment below.
Happy Coding 😉


0 comments:
Post a Comment
If you like this website, please share with your friends on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn.