In this article, I am going to discuss how to implement Basic Authentication Using Message Handler in ASP.NET Web API. Please read our last article, where I discussed the Server-Side HTTP Message Handler in ASP.NET Web API.
As we already discussed, the basic authentication says that the client needs to send the username and password in base64 encoded format in the authorization header of the HTTP request. The server then gets the username and password from the authorization header. Once the username and password get from the header, then the server check and match the credentials with any persistent storage (most of the time it may be a database). If the credentials are found in the persistent storage then the server will treat that HTTP request as a valid request and process it else it simple return unauthorized response to the client.
Let’s us implement Basic Authentication Using Message Handler
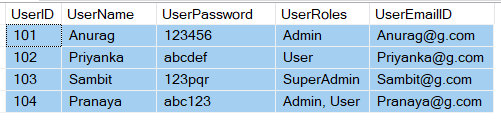
We are going to use the following UserMaster table in this demo
Please use below SQL Script to create and populate the UserMaster table with the required sample data.
Once you click on the OK button, it will create the application for us. Then the next step is to create an ADO.NET Entity Data Model against the SecurityDB and Select the UserMaster table.
Here you need to choose the DB First Approach of Entity Framework.
Let’s create a class with the name ValidateUser and copy and paste the following code.
Now, let’s implement our own custom message handler to check whether or not the client has sent an Authorization header along with the HTTP request, if it is presented then we will check the header value against the persistent storage, in our case, it’s the database table.
So let’s create a class with the name BasicAuthenticationMessageHandler and copy and paste the following code.
BasicAuthenticationMessageHandler.cs
If the Authorization header is not present in the HTTP request then it will be considered as a forbidden request but if it is present then we will get the header value. Once we get the header value then we need to decode as the value of the header is comes in encoded. Here we will use the Base64 encoding scheme in the attached header.
Once we get the user credentials then we will check the credentials and if the credentials are present in the database then we will consider it as a valid user and we will set the user principals along with the current thread.
The request will then be redirected towards a specific controller and action. Register the custom handler in the WebApiConfig file as shown in the below diagram.
That’s it. We are done with our implementation. Let’s create one empty Web API controller and then copy and paste the following code.
Testing using Postman
First, let’s test for the following user
UserName: Priyanka
Password: abcdef
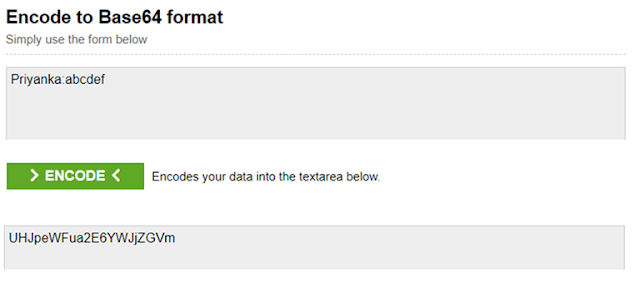
The username and password need to be a colon (:) separated and must be in base64 encoded. To do this use the following website
https://www.base64encode.org/
Enter the username and password separated by a colon (:) in “Encode to Base64 format” textbox, and then click on the “Encode” button as shown in the below diagram which will generate the Base64 encoded value.
Once you generated the Base64 encoded string, let’s see how to use basic authentication in the header to pass the Base64 encoded value.
Here we need to use the Authorization header and the value will be the Base64 encoded string as shown below.
Authorization: UHJpeWFua2E6YWJjZGVm
GET Request:
As you can see, we get Status 200 as expected as the user Priyanka has the role “User” and the role “User” has access to the Get Method of the Test Controller.
POST Request:
As you can see, we get Status 401 Unauthorized as expected as the user Priyanka has the role “User” and the role “User” does not have access to the Post Method of the Test Controller.
In the next article, I am going to discuss HTTP Client Message Handler with some examples. Here, in this article, I try to explain the Basic Authentication Using Message Handler step by step with an example. I hope this article will help you with your need. I would like to have your feedback. Please post your feedback, question, or comments about this article.
Summary:
I hope this post will be helpful to understand how to use Basic Authentication Using Message Handler in Web API
Please share this post with your friends and colleagues.
For any queries please post a comment below.
Happy Coding 😉
As we already discussed, the basic authentication says that the client needs to send the username and password in base64 encoded format in the authorization header of the HTTP request. The server then gets the username and password from the authorization header. Once the username and password get from the header, then the server check and match the credentials with any persistent storage (most of the time it may be a database). If the credentials are found in the persistent storage then the server will treat that HTTP request as a valid request and process it else it simple return unauthorized response to the client.
Let’s us implement Basic Authentication Using Message Handler
We are going to use the following UserMaster table in this demo
Please use below SQL Script to create and populate the UserMaster table with the required sample data.
CREATE DATABASE SECURIRT_DB GO USE [SECURIRT_DB] CREATE TABLE UserMaster ( UserID INT PRIMARY KEY, UserName VARCHAR(50), UserPassword VARCHAR(50), UserRoles VARCHAR(500), UserEmailID VARCHAR(100), ) GO INSERT INTO UserMaster VALUES(101, 'Anurag', '123456', 'Admin', 'Anurag@g.com') INSERT INTO UserMaster VALUES(102, 'Priyanka', 'abcdef', 'User', 'Priyanka@g.com') INSERT INTO UserMaster VALUES(103, 'Sambit', '123pqr', 'SuperAdmin', 'Sambit@g.com') INSERT INTO UserMaster VALUES(104, 'Pranaya', 'abc123', 'Admin, User', 'Pranaya@g.com') GOLet’s create an empty Web API application with the name BasicAuthenticationUsingMessageHandler (you can give any name) and select empty and Web API as shown in the below image.
Once you click on the OK button, it will create the application for us. Then the next step is to create an ADO.NET Entity Data Model against the SecurityDB and Select the UserMaster table.
Here you need to choose the DB First Approach of Entity Framework.
Let’s create a class with the name ValidateUser and copy and paste the following code.
namespace BasicAuthenticationUsingMessageHandler.Models
{
public class ValidateUser
{
//This method is used to check the user credentials
public UserMaster CheckUserCredentials(string username, string password)
{
// SECURIRT_DBEntities it is your context class
using (var context = new SECURIRT_DBEntities())
{
return context.UserMasters.FirstOrDefault(user =>
user.UserName.Equals(username, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase)
&& user.UserPassword == password);
}
}
}
}
In the above class, we create one method i.e. CheckUserCredentials which will validate the user by checking the username and password.
Now, let’s implement our own custom message handler to check whether or not the client has sent an Authorization header along with the HTTP request, if it is presented then we will check the header value against the persistent storage, in our case, it’s the database table.
So let’s create a class with the name BasicAuthenticationMessageHandler and copy and paste the following code.
BasicAuthenticationMessageHandler.cs
namespace BasicAuthenticationUsingMessageHandler.Models
{
public class BasicAuthenticationMessageHandler : DelegatingHandler
{
protected override Task<HttpResponseMessage> SendAsync(HttpRequestMessage request, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
try
{
var authenticationToken = request.Headers.GetValues("Authorization").FirstOrDefault();
if (authenticationToken != null)
{
byte[] data = Convert.FromBase64String(authenticationToken);
string decodedAuthenticationToken = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(data);
string[] UsernamePasswordArray = decodedAuthenticationToken.Split(':');
string username = UsernamePasswordArray[0];
string password = UsernamePasswordArray[1];
UserMaster ObjUser = new ValidateUser().CheckUserCredentials(username, password);
if (ObjUser != null)
{
var identity = new GenericIdentity(ObjUser.UserName);
identity.AddClaim(new Claim("Email", ObjUser.UserEmailID));
IPrincipal principal = new GenericPrincipal(identity, ObjUser.UserRoles.Split(','));
Thread.CurrentPrincipal = principal;
if (HttpContext.Current != null)
{
HttpContext.Current.User = principal;
}
return base.SendAsync(request, cancellationToken);
}
else
{
var response = new HttpResponseMessage(HttpStatusCode.Unauthorized);
var tsc = new TaskCompletionSource<HttpResponseMessage>();
tsc.SetResult(response);
return tsc.Task;
}
}
else
{
var response = new HttpResponseMessage(HttpStatusCode.BadRequest);
var tsc = new TaskCompletionSource<HttpResponseMessage>();
tsc.SetResult(response);
return tsc.Task;
}
}
catch
{
var response = new HttpResponseMessage(HttpStatusCode.Forbidden);
var tsc = new TaskCompletionSource<HttpResponseMessage>();
tsc.SetResult(response);
return tsc.Task;
}
}
}
}
Please add the following namespaces:
using System; using System.Linq; using System.Net; using System.Net.Http; using System.Security.Claims; using System.Security.Principal; using System.Text; using System.Threading; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Web;Explanation of the above code:
If the Authorization header is not present in the HTTP request then it will be considered as a forbidden request but if it is present then we will get the header value. Once we get the header value then we need to decode as the value of the header is comes in encoded. Here we will use the Base64 encoding scheme in the attached header.
Once we get the user credentials then we will check the credentials and if the credentials are present in the database then we will consider it as a valid user and we will set the user principals along with the current thread.
The request will then be redirected towards a specific controller and action. Register the custom handler in the WebApiConfig file as shown in the below diagram.
That’s it. We are done with our implementation. Let’s create one empty Web API controller and then copy and paste the following code.
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Threading;
using System.Web.Http;
namespace BasicAuthenticationUsingMessageHandler.Controllers
{
public class TestController : ApiController
{
[Authorize(Roles = "Admin,User")]
public HttpResponseMessage Get()
{
//You can implement your own logic
//Get the Identity Name
string username = Thread.CurrentPrincipal.Identity.Name;
return Request.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.OK, "User Name = "+ username);
}
[Authorize(Roles = "Admin")]
public HttpResponseMessage Post()
{
string username = Thread.CurrentPrincipal.Identity.Name;
return Request.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.OK, "User Name = " + username);
}
}
}
As you can see in the above controller, both the Get and Post are decorated with an Authorise attribute and we have specified the role over each action. So, the specific roles can access a specific action. Since the Get() is to read the data, generally both the Admin and the User can access it but a Post is only allowed for an Admin.
Testing using Postman
First, let’s test for the following user
UserName: Priyanka
Password: abcdef
The username and password need to be a colon (:) separated and must be in base64 encoded. To do this use the following website
https://www.base64encode.org/
Enter the username and password separated by a colon (:) in “Encode to Base64 format” textbox, and then click on the “Encode” button as shown in the below diagram which will generate the Base64 encoded value.
Once you generated the Base64 encoded string, let’s see how to use basic authentication in the header to pass the Base64 encoded value.
Here we need to use the Authorization header and the value will be the Base64 encoded string as shown below.
Authorization: UHJpeWFua2E6YWJjZGVm
GET Request:
As you can see, we get Status 200 as expected as the user Priyanka has the role “User” and the role “User” has access to the Get Method of the Test Controller.
POST Request:
As you can see, we get Status 401 Unauthorized as expected as the user Priyanka has the role “User” and the role “User” does not have access to the Post Method of the Test Controller.
In the next article, I am going to discuss HTTP Client Message Handler with some examples. Here, in this article, I try to explain the Basic Authentication Using Message Handler step by step with an example. I hope this article will help you with your need. I would like to have your feedback. Please post your feedback, question, or comments about this article.
Summary:
I hope this post will be helpful to understand how to use Basic Authentication Using Message Handler in Web API
Please share this post with your friends and colleagues.
For any queries please post a comment below.
Happy Coding 😉






0 comments:
Post a Comment
If you like this website, please share with your friends on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn.