In this article, I am going to discuss how to create Custom Method Names in Web API application. Please read our previous article before proceeding to this article where we discussed how to implement the CRUD Operation in ASP.NET Web API Application and we are also going to work with the same example.
Understanding the Default Convention used by ASP.NET Web API.
Let’s understand the default convention used by ASP.NET Web API to map HTTP verbs GET, PUT, POST and DELETE to methods in a controller with an example.
By default, the HTTP verb GET is mapped to a method in a controller that has the name Get() or starts with the word Get.
In the following EmployeesController, the method name is Get() so by default convention, this is mapped to the HTTP verb GET. Even if we rename it to GetEmployees() or GetSomething() it will still be mapped to the HTTP verb GET as long as the name of the method is prefixed with the word Get. The word Get is case-insensitive. It can be lowercase, uppercase or a mix of both.
If the method is not named as GET or if it does not start with the word GET then Web API does not know the method name to which, the GET request must be mapped and the request fails with an error message stating The requested resource does not support HTTP method ‘GET’ with the status code 405 Method Not Allowed.
In the following example, we have renamed Get() method to LoadAllEmployees(). When we issue a GET request the request will fail because ASP.NET Web API does not know it has to map the GET request to this method.
To instruct Web API to map HTTP verb GET to LoadAllEmployees() method, decorate the method with [HttpGet] attribute as shown below.
Let’s say we have the following two methods in our Employee API controller.
When we navigate to the URI /api/employees/1
Notice, we are getting all the Employees, instead of just the Employee with Id=1. This is because in this case the GET request is mapped to LoadAllEmployees() and not to LoadEmployeeById(int id).
If you want the GET request to be mapped to LoadEmployeeById(int id) when the id parameter is specified in the URI, then decorate the LoadEmployeeById(int id) method also with [HttpGet] attribute as shown below.
That’s OK. But in real-time we may have to implement multiple get or post or put method within a single controller. For example, we have two methods as shown below
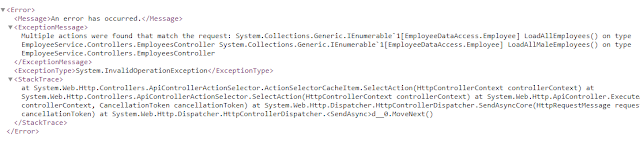
Now when we make a request with the URL /api/employees We will get the below error
Now the question is how to access these two methods along with how we will provide a unique URL to each resource.
First, let’s see the default implementation of the WebApiConfig class which is present in App_Start Folder.
The default route specifies the URL route as domain Name Followed by API and controller name. In our example, it will be http://localhost:xxxxx/api/employees where “employees” is the controller name.
Implementing Custom Method Names in Web API:
To implement Custom Method Names in Web API, Let’s change first the default implementation of the WebApiConfig class as shown below where we include the action name as part of the route.
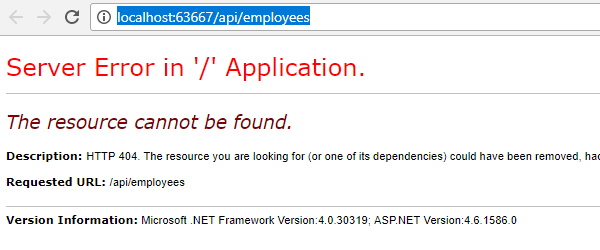
Now make a request with the same URL /api/employees It will give us the following error
So change the URL as we need to include the action name in the URL as we do the changes in the WebApiConfig class.
/api/employees/LoadAllEmployees
/api/employees/LoadAllMaleEmployees
That’s it. We have successfully implemented Custom Method Names in Web API. Now you will get the response as expected.
Summary:
I Hope this post will be helpful to understand the concept of Custom Method Names in Web API.
Please share this post with your friends and colleagues.
For any queries please post a comment below.
Happy Coding 😉
Understanding the Default Convention used by ASP.NET Web API.
Let’s understand the default convention used by ASP.NET Web API to map HTTP verbs GET, PUT, POST and DELETE to methods in a controller with an example.
By default, the HTTP verb GET is mapped to a method in a controller that has the name Get() or starts with the word Get.
In the following EmployeesController, the method name is Get() so by default convention, this is mapped to the HTTP verb GET. Even if we rename it to GetEmployees() or GetSomething() it will still be mapped to the HTTP verb GET as long as the name of the method is prefixed with the word Get. The word Get is case-insensitive. It can be lowercase, uppercase or a mix of both.
public class EmployeesController : ApiController
{
public HttpResponseMessage Get()
{
using (EmployeeDBContext dbContext = new EmployeeDBContext())
{
var Employees = dbContext.Employees.ToList();
return Request.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.OK, Employees);
}
}
}
If the method is not named as GET or if it does not start with the word GET then Web API does not know the method name to which, the GET request must be mapped and the request fails with an error message stating The requested resource does not support HTTP method ‘GET’ with the status code 405 Method Not Allowed.
In the following example, we have renamed Get() method to LoadAllEmployees(). When we issue a GET request the request will fail because ASP.NET Web API does not know it has to map the GET request to this method.
public class EmployeesController : ApiController
{
public HttpResponseMessage LoadAllEmployees()
{
using (EmployeeDBContext dbContext = new EmployeeDBContext())
{
var Employees = dbContext.Employees.ToList();
return Request.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.OK, Employees);
}
}
}
To instruct Web API to map HTTP verb GET to LoadAllEmployees() method, decorate the method with [HttpGet] attribute as shown below.
public class EmployeesController : ApiController
{
[HttpGet]
public HttpResponseMessage LoadAllEmployees()
{
using (EmployeeDBContext dbContext = new EmployeeDBContext())
{
var Employees = dbContext.Employees.ToList();
return Request.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.OK, Employees);
}
}
}
Let’s say we have the following two methods in our Employee API controller.
public class EmployeesController : ApiController
{
[HttpGet]
public HttpResponseMessage LoadAllEmployees()
{
using (EmployeeDBContext dbContext = new EmployeeDBContext())
{
var Employees = dbContext.Employees.ToList();
return Request.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.OK, Employees);
}
}
public HttpResponseMessage LoadEmployeeByID(int id)
{
using (EmployeeDBContext dbContext = new EmployeeDBContext())
{
var entity = dbContext.Employees.FirstOrDefault(e => e.ID == id);
if (entity != null)
{
return Request.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.OK, entity);
}
else
{
return Request.CreateErrorResponse(HttpStatusCode.NotFound,
"Employee with ID " + id.ToString() + "not found");
}
}
}
}
When we navigate to the URI /api/employees/1
Notice, we are getting all the Employees, instead of just the Employee with Id=1. This is because in this case the GET request is mapped to LoadAllEmployees() and not to LoadEmployeeById(int id).
If you want the GET request to be mapped to LoadEmployeeById(int id) when the id parameter is specified in the URI, then decorate the LoadEmployeeById(int id) method also with [HttpGet] attribute as shown below.
public class EmployeesController : ApiController
{
[HttpGet]
public HttpResponseMessage LoadAllEmployees()
{
using (EmployeeDBContext dbContext = new EmployeeDBContext())
{
var Employees = dbContext.Employees.ToList();
return Request.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.OK, Employees);
}
}
[HttpGet]
public HttpResponseMessage LoadEmployeeByID(int id)
{
using (EmployeeDBContext dbContext = new EmployeeDBContext())
{
var entity = dbContext.Employees.FirstOrDefault(e => e.ID == id);
if (entity != null)
{
return Request.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.OK, entity);
}
else
{
return Request.CreateErrorResponse(HttpStatusCode.NotFound,
"Employee with ID " + id.ToString() + "not found");
}
}
}
}
That’s OK. But in real-time we may have to implement multiple get or post or put method within a single controller. For example, we have two methods as shown below
public class EmployeesController : ApiController
{
[HttpGet]
public HttpResponseMessage LoadAllEmployees()
{
using (EmployeeDBContext dbContext = new EmployeeDBContext())
{
var Employees = dbContext.Employees.ToList();
return Request.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.OK, Employees);
}
}
[HttpGet]
public HttpResponseMessage LoadAllMaleEmployees()
{
using (EmployeeDBContext dbContext = new EmployeeDBContext())
{
var Employees = dbContext.Employees.Where(x => x.Gender == "Male").ToList();
return Request.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.OK, Employees);
}
}
}
Now when we make a request with the URL /api/employees We will get the below error
Now the question is how to access these two methods along with how we will provide a unique URL to each resource.
First, let’s see the default implementation of the WebApiConfig class which is present in App_Start Folder.
public static class WebApiConfig
{
public static void Register(HttpConfiguration config)
{
// Web API routes
config.MapHttpAttributeRoutes();
config.Routes.MapHttpRoute(
name: "DefaultApi",
routeTemplate: "api/{controller}/{id}",
defaults: new { id = RouteParameter.Optional }
);
}
}
The default route specifies the URL route as domain Name Followed by API and controller name. In our example, it will be http://localhost:xxxxx/api/employees where “employees” is the controller name.
Implementing Custom Method Names in Web API:
To implement Custom Method Names in Web API, Let’s change first the default implementation of the WebApiConfig class as shown below where we include the action name as part of the route.
public static class WebApiConfig
{
public static void Register(HttpConfiguration config)
{
// Web API routes
config.MapHttpAttributeRoutes();
config.Routes.MapHttpRoute(
name: "DefaultApi",
routeTemplate: "api/{controller}/{action}/{id}",
defaults: new { id = RouteParameter.Optional }
);
}
}
Now make a request with the same URL /api/employees It will give us the following error
So change the URL as we need to include the action name in the URL as we do the changes in the WebApiConfig class.
/api/employees/LoadAllEmployees
/api/employees/LoadAllMaleEmployees
That’s it. We have successfully implemented Custom Method Names in Web API. Now you will get the response as expected.
Summary:
I Hope this post will be helpful to understand the concept of Custom Method Names in Web API.
Please share this post with your friends and colleagues.
For any queries please post a comment below.
Happy Coding 😉


0 comments:
Post a Comment
If you like this website, please share with your friends on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn.